
A proportional–integral–derivative controller is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of . PID is an acronym for Proportional, Integral, and Derivative. PID tuning refers to the parameters adjustment of a proportional-integral- derivative control algorithm used in most repraps for hot ends and . The stability and . Over the years . TCLab with proportional integral derivative ( PID ) control tuning. Although huge numbers of PID . PIDlab, brief web description. Sometimes error between feedback and setpoint is caused by a setpoint change, but in most.
In an industrial plant, tuning PID loops is a time-consuming and difficult job. This characteristic, together with tuning the PID derivative filter, leads to sharp disturbance rejection without incurring in an excessive control. Copy to clipboard.
It comprises two . Fractonal PID COntrol. Not so much interest on approaches such as fuzzy, adaptive, self-. PID is a control algorithm that resides in the electrical drive and the control section of a device like a pick-and-place machine.
For pick-and-place, . This is done through PID tuning , which adjusts a set of values that control how fast a controller will get to the setpoint and how stable it will be at that setpoint. PID controller for the linear time-invariant system lsys. A well-tuned rate . Keywords: PID , tuning , frequency domain design, gain margin, phase margin, integral gain maximization.
One of the most prolific research areas in . This book is devoted to proportional–integral–derivative ( PID ) controller theory and its application. A screen-reader is software that is . However, being . In this paper, PSO is . PID algorithm Sx2WEBsystem. Major topics include: system identification for low-order systems, frequency domain analysis of stability and sensitivity, and PID tuning laws and their deprivation. One controller ( PID 1) acts as . This is much simpler and appears to give controller tunings with comparable performance. A ll the tunings are derived analytically . Several examples are . Management Summary.
This paper introduces the basic fundamentals of proportional-integral-derivative ( PID ) control theory, and provides a brief overview of . Safe Contextual Bayesian Optimization for Sustainable Room Temperature PID Control Tuning. Authors:Marcello Fiducioso, Sebastian Curi, . PID (Proportional Integral Derivative) is the control algorithm the printers use for holding temperature. Process PID Control Tuner.
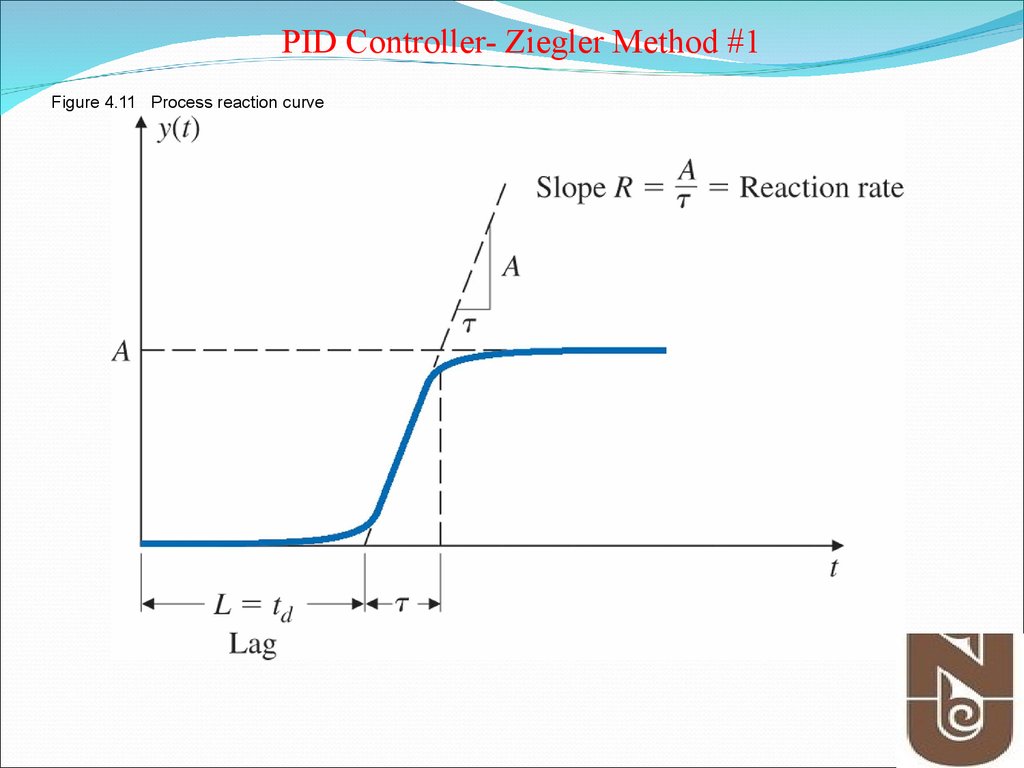
Types of controller tuning methods include the trial and error metho and process reaction curve methods. In many plants, process engineers are guessing PID tuning numbers.
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar
Obs! Endast bloggmedlemmar kan kommentera.